Overview of Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) have transformed the automotive market. They’ve evolved from niche products to mainstream options. These vehicles incorporate advanced battery technology and improved charging infrastructure. EVs now offer performance, efficiency, and sustainability.
Types of Electric Vehicles
There are several types of EVs available:
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs): BEVs run entirely on electricity stored in their batteries. They produce no tailpipe emissions—examples include the Tesla Model S and Nissan Leaf.
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs): PHEVs combine a conventional internal combustion engine with an electric motor. They can run on electricity for limited distances before switching to gasoline—examples include the Chevrolet Volt and Toyota Prius Prime.
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs): HEVs primarily use a gasoline engine supplemented by an electric motor for better fuel efficiency. Unlike PHEVs, they can’t be plugged in to recharge—examples include the Toyota Prius and Honda Insight.
Advancements in Battery Technology
Modern EVs benefit from advancements in battery technology. Lithium-ion batteries remain the industry standard, offering higher energy density, faster charging, and longer life cycles. Researchers are exploring solid-state batteries, which promise even greater performance and safety.
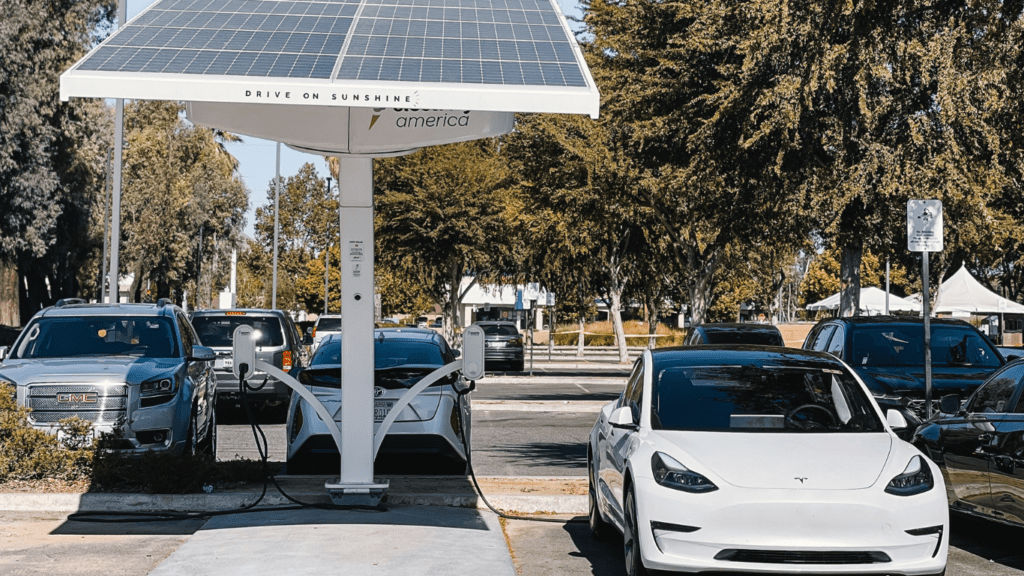
Charging Infrastructure Improvements
Charging infrastructure has seen significant improvements. Public charging stations are ubiquitous in urban areas. Fast-charging stations can recharge an EV’s battery up to 80% in less than 30 minutes. Home charging solutions are also more accessible, with many EV owners opting for Level 2 chargers for faster charging overnight.
Government Incentives and Policies
Many governments support EV adoption through incentives and policies. These include tax rebates, purchase subsidies, and exemptions from congestion charges. Examples are the federal tax credit for electric cars in the US and the Plug-in Car Grant in the UK.
Sustainability and Environment
EVs contribute significantly to sustainability efforts. They reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. When charged with renewable energy, their environmental impact is even lower. Countries are increasingly investing in renewable energy sources to complement the shift to electric vehicles.
Innovations and Future Trends
The future of EVs looks promising with continued innovations. Autonomous driving technology, vehicle-to-grid (V2G) systems, and wireless charging are noteworthy advancements. Automakers are also focusing on creating more affordable EVs to broaden consumer accessibility.
Electric vehicles represent a major shift in the automotive market. With these advancements and innovations, they are set to become the standard choice for eco-conscious drivers.
Recent Technological Advances

Electric vehicles have seen remarkable technological advancements in recent years, driving the automotive market forward.
Battery Innovations
Battery innovations have transformed EV performance and efficiency. Lithium-ion batteries dominate due to their high energy density. Manufacturers are investing in solid-state batteries, which offer higher energy densities and faster charging times. QuantumScape, a notable player, aims to commercialize solid-state batteries by 2025. These batteries promise safety improvements since they reduce the risk of overheating.
Recycling technologies have also advanced. Companies like Redwood Materials are developing methods to recycle and reuse key battery components, reducing reliance on raw materials and lessening environmental impact. Emerging battery designs, like silicon anode batteries, improve capacity and reduce charging times, addressing common consumer concerns about range and downtime.
Charging Infrastructure
Charging infrastructure improvements enhance convenience for EV owners. The number of public charging stations has increased substantially, with over 100,000 in the US alone. Companies like ChargePoint and EVgo lead this expansion, offering Level 2 and DC fast chargers that significantly reduce charging times.
Home charging solutions are more affordable and efficient. Smart chargers, integrated with home energy management systems, optimize energy use and reduce costs. Solar-powered charging stations are another innovative solution. Tesla’s Solar Roof, combined with Powerwall batteries, provides a sustainable way to charge EVs at home, leveraging renewable energy and reducing grid dependency.
Technological advances in vehicle-to-grid (V2G) systems enable EVs to discharge energy back to the grid, offering benefits like grid stabilization and potential income for EV owners. This bi-directional charging technology represents a paradigm shift in how we think about energy consumption and storage.
Recent improvements ensure that EVs are more accessible, practical, and environmentally friendly. These advancements underscore the pivotal role of innovation in propelling the automotive market into a sustainable future.
Market Trends
Electric vehicle (EV) adoption is accelerating, driven by technological advancements and sustainability efforts. Let’s explore key trends shaping the market.
Sales and Adoption Rates
Recent data shows exponential growth in EV sales. In 2022, global EV sales surpassed 10 million units, marking a 30% increase from 2021 (source: IEA). Countries like China, Norway, and the US lead in EV market penetration, with notable sales figures from manufacturers such as Tesla, Nissan, and Volkswagen.
Government Policies and Incentives
Government policies are crucial in promoting EV adoption. The US offers federal tax credits up to $7,500 for new EV purchases. European countries like Germany and France provide substantial purchase subsidies and tax exemptions, enhancing affordability. Additionally, states like California implement stringent emission regulations, pushing automakers toward electrification.
These market trends indicate a robust trajectory for electric vehicles, driven by supportive policies and increasing consumer demand.
Key Players in the Market
Several companies are making significant strides in the electric vehicle (EV) sector. Let’s explore the established automakers and emerging startups driving this transformation.
Established Automakers
- Tesla: Tesla spearheads the EV market with innovative models like the Model S, Model 3, and Model Y. Tesla’s extensive Supercharger network ensures convenient charging for customers, boosting its market dominance.
- Nissan: Nissan remains a key player with the Nissan Leaf, one of the best-selling electric cars worldwide. The company continues to innovate with its ProPILOT driver assistance technology.
- Volkswagen: Volkswagen’s ID. series, including the ID.4, showcases its commitment to an electric future. The company plans to launch 75 new EV models by 2029.
- BMW: BMW’s i4 and iX models highlight its focus on luxury EVs. By 2030, BMW aims for half of its global sales to consist of fully electric vehicles.
- General Motors (GM): GM pushes forward with its Ultium battery technology. Models like the Chevrolet Bolt and the upcoming Hummer EV are integral to GM’s electric strategy.
- Rivian: Rivian focuses on electric adventure trucks, with the R1T truck and R1S SUV already generating significant interest. Contracts with companies like Amazon highlight Rivian’s potential.
- Lucid Motors: Lucid’s Air sedan promises high performance and luxury, with an impressive range of over 500 miles per charge. Lucid aims to challenge Tesla’s market position.
- Nio: Based in China, Nio targets innovative battery swap stations, enabling quick and efficient charging. Nio’s ES6 and ES8 models gain popularity for their premium features.
- Fisker Inc.: Fisker plans to deliver sustainable vehicles with its Ocean SUV. The company’s mission focuses on affordability and using recycled materials in manufacturing.
- Canoo: Canoo’s unique approach includes modular electric vehicles for consumer and commercial use. Its subscription model aims to transform vehicle ownership.
These key players, both established giants and agile startups, shape the evolving landscape of the EV market.
Consumer Perspectives
Consumers are increasingly considering electric vehicles (EVs) for various reasons. Many weigh the benefits against common concerns and misconceptions.
Benefits of Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles offer numerous advantages. They’re environmentally friendly, producing zero tailpipe emissions. Reduced greenhouse gases and improved air quality benefit public health. EVs also have lower operating costs compared to gasoline vehicles. For instance, charging an EV generally costs less than refueling a traditional car. Additionally, EVs require less maintenance. Without an internal combustion engine, there’s no need for oil changes, and their simpler drivetrains have fewer parts that might fail.
Common Concerns and Misconceptions
Despite the benefits, some consumers hesitate. A common concern is range anxiety. Many believe EVs can’t travel far enough on a single charge. However, most modern EVs offer ranges of over 200 miles, which meets daily driving needs for the majority of users. Another misconception is that charging infrastructure isn’t sufficient. While this was true a decade ago, the number of public chargers has surged. With over 100,000 public charging stations in the US alone, accessing a charge is easier than ever. Lastly, some think EVs are too expensive. Though the upfront cost can be higher, tax rebates, subsidies, and lower operational costs often offset this.
Future Outlook
The future of electric vehicles (EVs) looks promising, driven by rapid technological advancements and increasing consumer interest. Key areas like autonomous driving and vehicle-to-grid systems are set to revolutionize the EV market.
Predictions and Projections
Experts predict the continued growth of the EV market, with global sales expected to surpass 30 million units by 2030. Major automakers plan significant investments in electric mobility, boosting production capacities and diversifying model offerings. Battery costs are likely to drop by 50% by 2030, driven by advancements like solid-state batteries. Solar-powered charging stations will become more prevalent, supporting the integration of renewable energy.
Potential Challenges
Despite the optimistic outlook, the EV market faces several challenges. Charging infrastructure needs expansion to support the growing number of EVs on the road. Lithium supply for batteries might become constrained, affecting production scalability. Additionally, the high initial cost remains a barrier for many consumers, although government incentives are helping to mitigate this issue. Policies must evolve to keep pace with technological advancements and market demands.